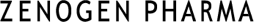Adjuvant
For inquires including COA (certificate of analysis), please send message to following e-mail address.
zenogen_pharma-post@zenoaq.jp
ZenoParticle CH-100
- Product
-
Product Name Package, Storage ZenoParticle CH-100 5 X 500µL,
Refrigeration (2-8℃)
- Features
-
Properties of ZenoParticle;
- Micronized chitosan (polysaccharide) formed by our original technology
- Easier to mix with antigen than oil-based adjuvant
- Made of biodegradable materials, which are not harmful
- Not irritant at injection site and suitable for multiple administration
Adjuvant effects of ZenoParticle;
- Instruction for use
-
- Prepare an antigen solution using saline etc. (Needed volume of the solution equals to that of ZenoParticle to be used. Adjust concentration of an antigen solution according to characteristics of the antigen. Precipitation may occur if concentration of the antigen is too high or characteristics of the antigen is not suitable. As an example, in the studies presented below, 20 µg/ml OVA [Ovalbumin] solution was prepared as an antigen solution.)
- Bring a tube of ZenoParticle from refrigeration to room temperature and stir. (Using a vortex mixer recommended)
- Mix the prepared antigen solution and ZenoParticle in a 1:1 ratio.
- Stir the mixture at room temperature. (Using a vortex mixer recommended)
- Use immediately after checking the mixture is sufficiently stirred.
(As an example, 100 to 200 µl of injection is suitable for intraperitoneal administration in mice.)
Persistent antibody production is induced in various administration routes.
- Result 1:
-
Intraperitoneal administration to mice induced persistent elevation of serum antibody titer.
Five-week-old female BALB/c mice (n=5) were immunized by intraperitoneal injection of 1µg OVA with ZenoParticle or Alum. After 2 times injection at 2 week interval, anti-OVA antibody titer in serum was evaluated over time by ELISA.
Elevation of antibody titer observed one week after 2 times injection persisted, and observed similarly 46 weeks after immunization. - Result 2:
-
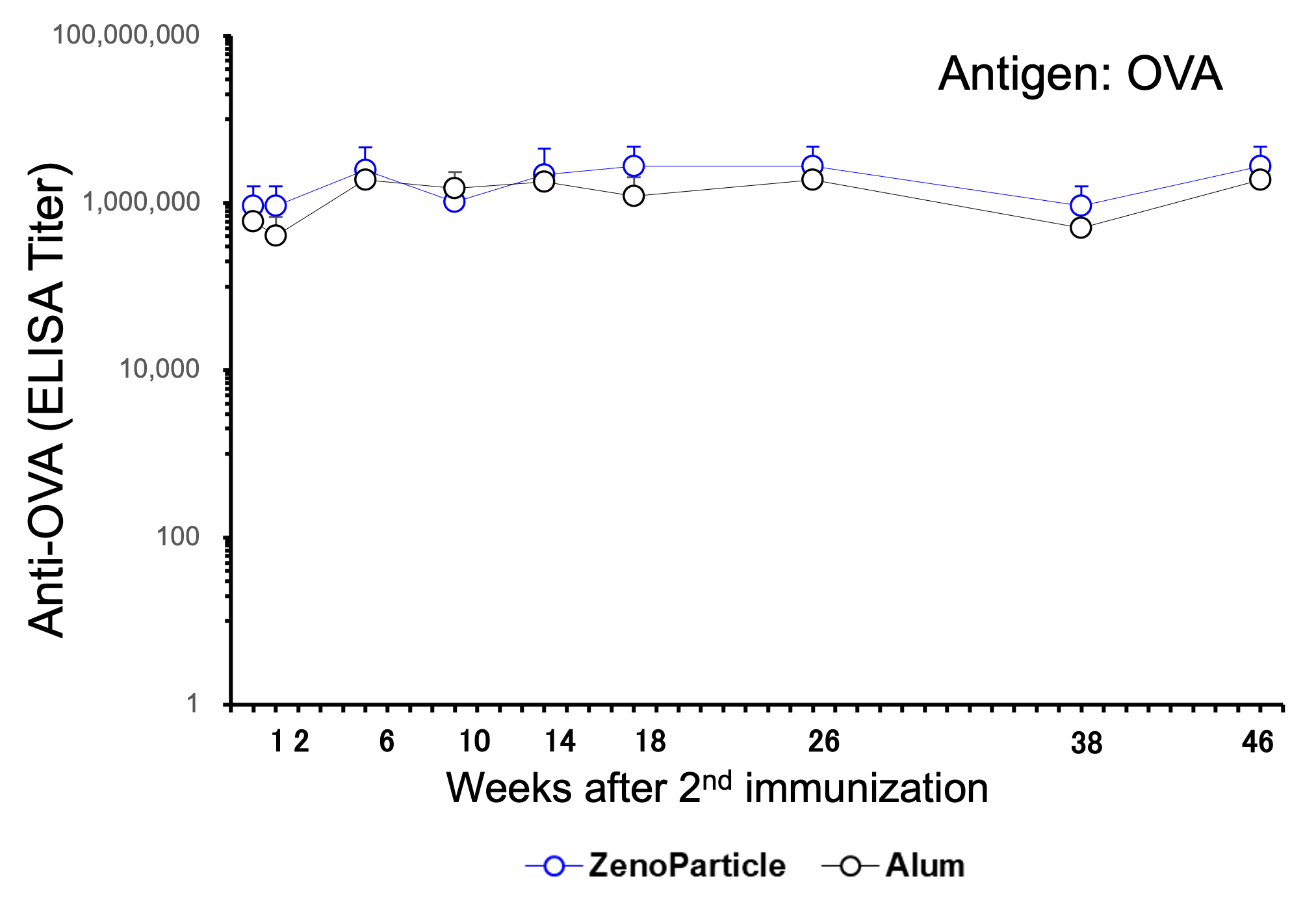
Intradermal, subcutaneous and intramuscular administration induced persistent elevation of serum antibody titer.
Five-week-old female BALB/c mice (n=5) were immunized by intraperitoneal injection of 1µg OVA with ZenoParticle or Alum. Immunization by intradermal or subcutaneous or intramuscular injection was performed 3 times at 2 week intervals.. Anti-OVA antibody titer in serum was evaluated by ELISA at 1 week after 2nd immunization and 1/4/8 weeks after 3rd immunization.
Each route of administration (intradermal, subcutaneous or intramuscular) represented persistent elevation of serum antibody titer similar to intraperitoneal administration.
Immunostimulation is confirmed in tumor grafted mouse model.
- Result 3:
-
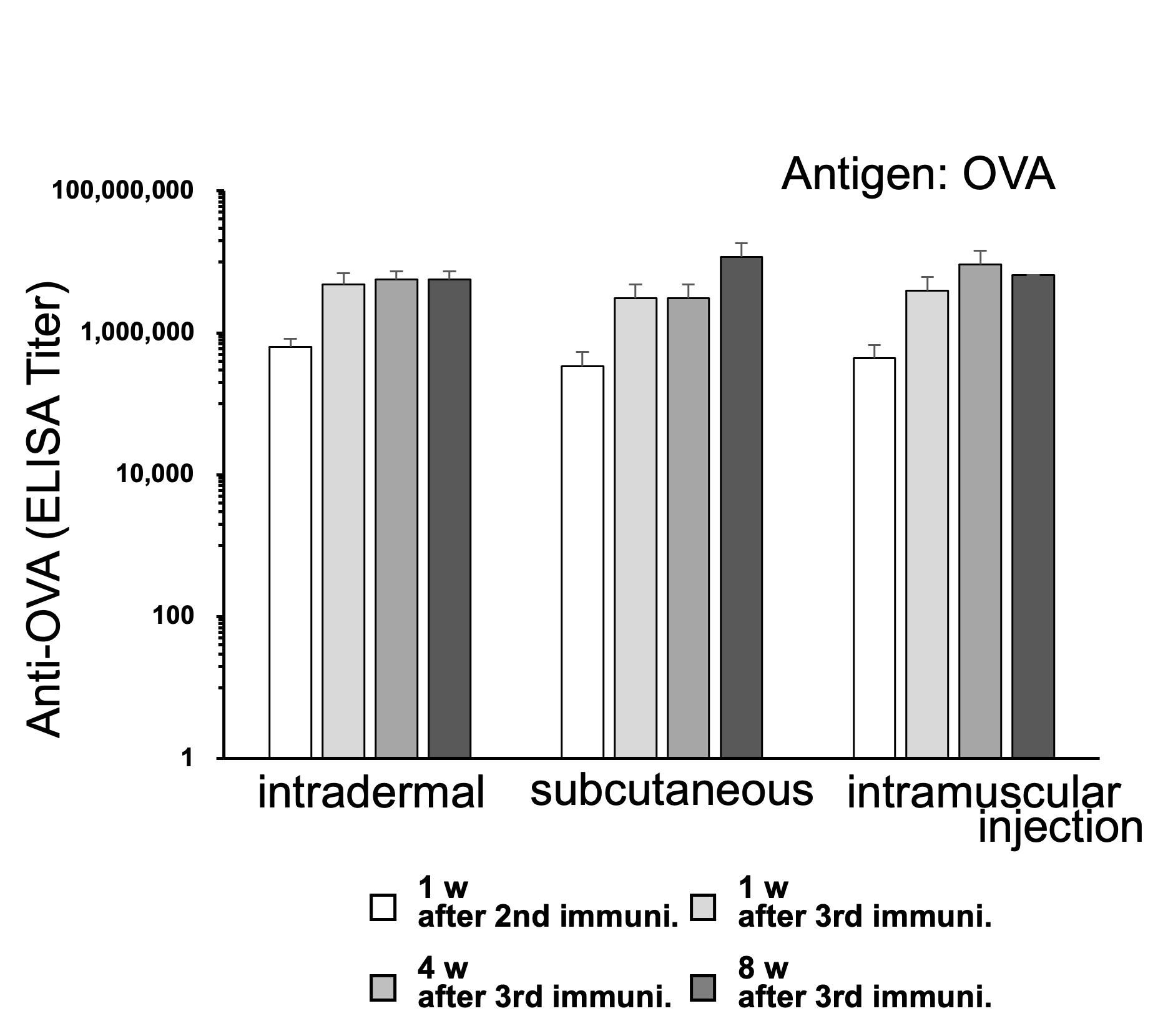
Antigen specific IgG production and tumor growth suppression were observed after antigen immunization in tumor grafted model mice.
Eight-week-old female C57BL/6 mice (n=5) were immunized by subcutaneous injection of 100 µg OVA with ZenoParticle or Alum. OVA expressed B16F10 melanoma (2x105 cells) were subcutaneously implanted twelve days after the first immunization. The second immunization was performed two days after the implantation.
Results of serum OVA titer and tumor weight evaluation 28 days after the first immunization (14 days after the second immunization) represented antigen specific IgG production and tumor growth suppression. ZenoParticle represented more significant effects than Alum adjuvant.
(Provided from collaborating Labs.)
Antibody production is confirmed when administered with antigens such as peptides or virus-derived proteins.
- Result 4:
-
Immunization with virus-derived protein represented persistent elevation of serum antibody titer.
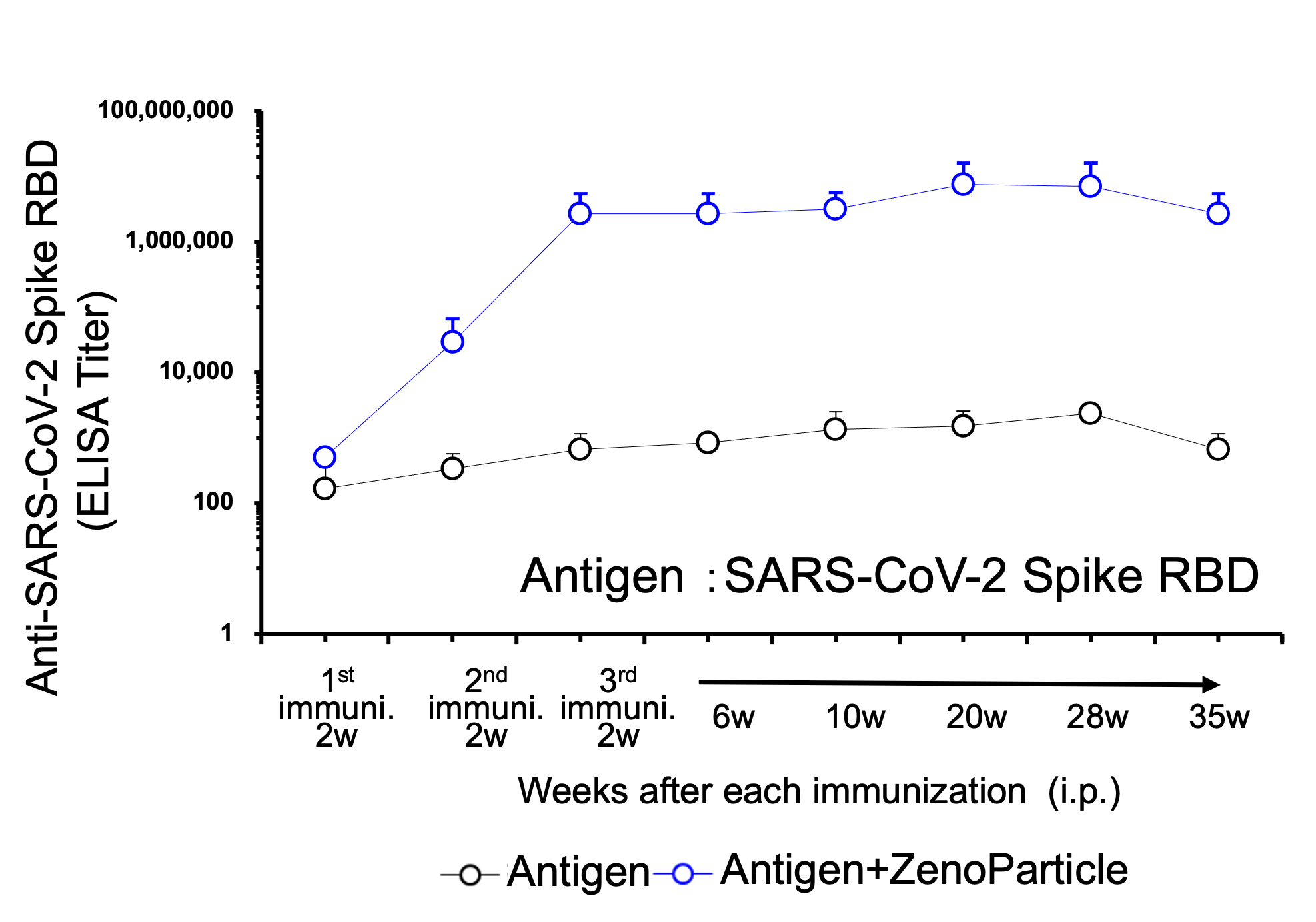
Eight-week-old female BALB/c mice (n=5) were immunized 3 times by intraperitoneal injection of antigen protein (1st; 20µg, 2nd & 3rd; 10µg) with or without ZenoParticle. 2nd immunization was performed 2 weeks after 1st immunization, and 3rd immunization was performed 5 weeks after 2nd immunization. Antibody titer in serum was evaluated by ELISA at 2 weeks after 1st immunization, 2 weeks after 2nd immunization, and 2/6/10/20./28/35 weeks after 3rd immunization.
Elevation of antibody titer was observed from 2 weeks after 2nd immunization and the elevation persisted from 2 weeks to 35 weeks after 3rd immunization. - Result 5:
-
Serum antibody titer elevated early and persisted long after immunization.
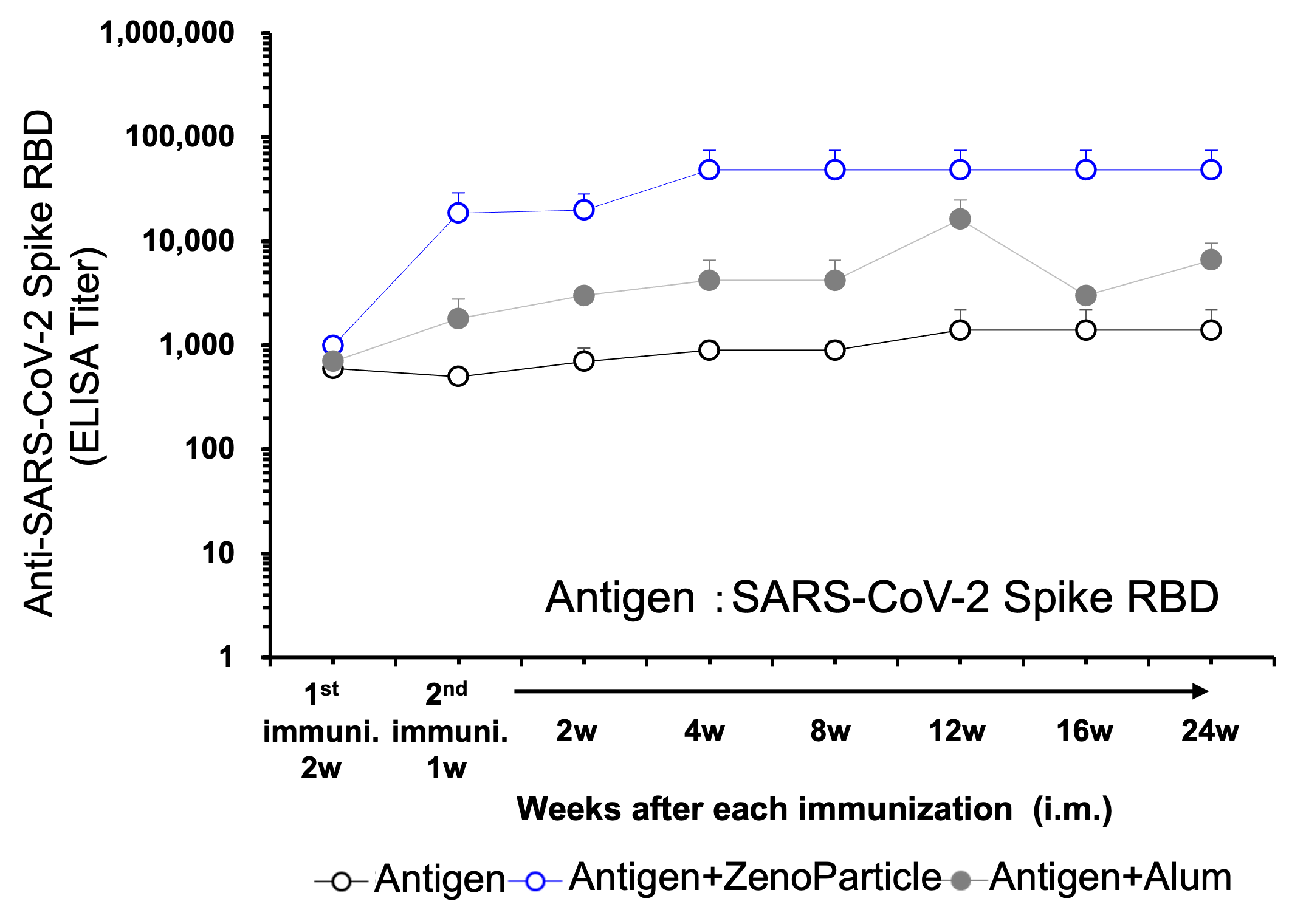
Eight-week-old female BALB/c mice (n=5) were immunized by intramuscular injection (2 times at 2 week interval) of antigen protein (10µg) with ZenoParticle or Alum. Antibody titer in serum was evaluated by ELISA from 2 weeks after 1st immunization.
Elevation of antibody titer was observed from 1 week after 2nd immunization and the elevation persisted 24 weeks after 2nd immunization. Immunization with ZenoParticle represented higher titer than with Alum. - Result 6:
-
Immunization of rats with hormone peptide represented elevation of serum antibody titer.
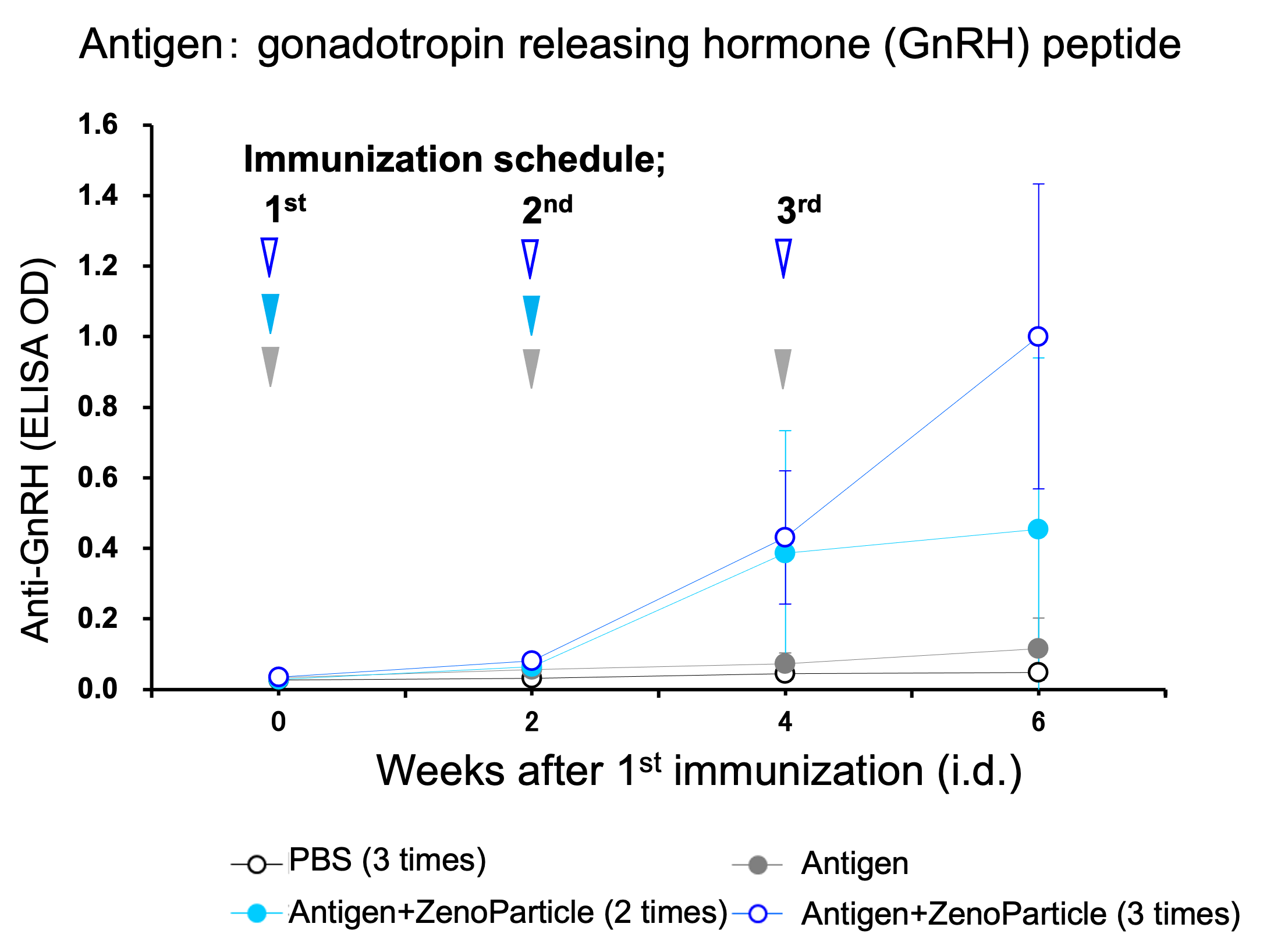
Nine-week-old male rats (Wistar Imamichi) (n=4) were immunized by intradermal injection (3 times at 2 week intervals) of 100µg antigen with or without ZenoParticle. Anti-GnRH antibody titer in serum after 1st immunization was periodically evaluated by ELISA.
Elevation of antibody titer observed 2 weeks after 2nd immunization, and the elevation became higher according to times of immunization.
References
- 1)Development of a seroepidemiological tool for bat-borne and shrew-borne hantaviruses and its application using samples from Zambia.
Sarii RS, Kajihara M, Wei Z, Lokpathirage SMW, Muthusinghe DS, Mori-Kajihara A, Changula K, Qiu Y, Ndebe J, Hang'ombe BM, Kikuchi F, Hayashi A, Suzuki M, Kamiya H, Arai S, Takada A, Yoshimatsu K. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Nov 21;18(11):e0012669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012669. eCollection 2024 Nov. - 2)The Chitosan Nanoparticle-based Adjuvant CH-100 Orchestrates Multifaceted Innate Immune Activation via STING-Dependent and -Independent Pathways.
Nagai E, Ori D, Kano N, Ikegawa M, Kobiyama K, Ishii KJ, Kawasaki T, Kawai T. Int Immunol. 2025 Sep 15:dxaf054. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxaf054.